Most Common Reasons for Physical Therapy
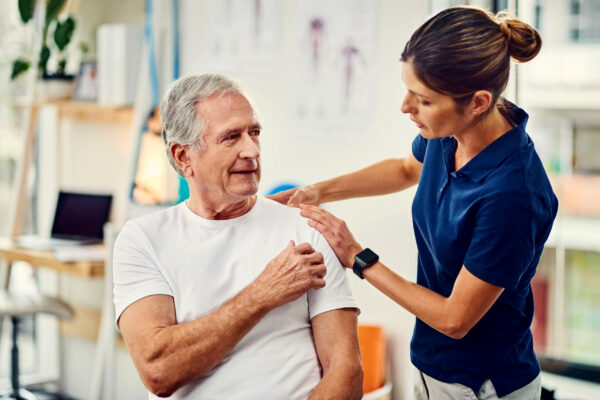
There are more benefits than you may realize
Physical therapy is a proven treatment method that helps people heal from injuries, disabilities, and health conditions. Some of its many benefits include pain management, improved mobility, and muscle strengthening. This article will outline some of the most common reasons for physical therapy and how you can receive therapy from the comfort of your home.
How physical therapy supports your unique needs
Each person’s needs and goals for physical therapy are unique. After a therapist does an evaluation of your condition and reviews your medical history, together you will establish short and long-term goals. The therapist will then work with you to create a plan to help you meet those goals. Exercise is a main component of physical therapy, but recommended treatments may also include posture correction and alignment, balance and coordination training, and stress-relieving routines.
Here are 7 of the most common reasons for physical therapy
Manage pain:
Therapeutic exercises and therapy techniques can help relieve pain and restore muscle and joint function. Physical therapy can help reduce or eliminate the use of opioids for pain relief.
Improve mobility:
Stretching and strengthening exercises help restore your ability to move better at any age. Whether you have a chronic condition like arthritis, are recovering from an injury or surgery, or are managing age-related mobility issues, physical therapy may help.
Avoid surgery:
If physical therapy helps you manage pain or heal from an injury, surgery may not be needed. If you do need surgery, pre-surgery therapy can help you go into surgery in better shape, and post-surgery therapy can help speed recovery.
Recover from an injury:
Physical therapists can design recovery or prevention exercise programs to help you recover from or prevent injury. Some injuries that can be treated during physical therapy include tennis elbow, groin pulls, shin splints, hamstring strains, shoulder injuries, sprained ankles, knee injuries, Achilles tendinitis and more.
Recover from a stroke:
Physical therapy helps strengthen weakened parts of the body and improve posture and balance after having a stroke. Therapists can also improve stroke patients’ ability to be more independent by helping them return to performing everyday tasks.
Prevent falls:
Physical therapy can improve coordination and balance, which reduces the likelihood of falls. Physical and occupational therapists can work together to recommend assistive devices and provide training on the proper way to use these devices to improve safety and reduce fall risk.
Manage a chronic illness:
In addition to treating ailments such as arthritis and injuries, physical therapists can work with other healthcare professionals such as nurses and occupational and speech therapists to help manage chronic illnesses, such as Parkinson’s Disease, Congestive Heart Failure (CHF), diabetes, and more.
Regardless of your reason for starting physical therapy, being patient and persistent is the best way to see lasting results and continued improvement.
In-home therapy
Ethos Home Health Care provides in-home physical, occupational, and speech therapy to help individuals maintain or regain independence at home. If you think in-home therapy might be right for you or a loved one, take our free online assessment to learn more about care needs and if home health care would be a good fit. For additional questions, fill out an online form, or call (701) 809-9319 to speak with a member of our team.
Published on October 25th, 2023
Copyright 2021-2023 © Baldwin Publishing, Inc. Health eCooks® is a registered trademark of Baldwin Publishing, Inc. Cook eKitchen™ is a designated trademark of Baldwin Publishing, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein without the express approval of Baldwin Publishing, Inc. is strictly prohibited.
Date Last Reviewed: August 12, 2021
Editorial Review: Andrea Cohen, Editorial Director, Baldwin Publishing, Inc. Contact Editor
Medical Review: Andrew Overman, DPT, MS, COMT, CSCS
Learn more about Baldwin Publishing Inc. editorial policy, privacy policy, ADA compliance and sponsorship policy.
No information provided by Baldwin Publishing, Inc. in any article is a substitute for medical advice or treatment for any medical condition. Baldwin Publishing, Inc. strongly suggests that you use this information in consultation with your doctor or other health professional. Use or viewing of any Baldwin Publishing, Inc. article signifies your understanding and agreement to the disclaimer and acceptance of these terms of use.